힙(Heaps) 구조란?
👉 힙은 트리처럼 생긴 데이터 구조이다. 다른 트리형 데이터 구조와는 달리 자식을 가리키는 포인터 대신 데이터를 배열에다 저장한다. 따라서 인덱스를 활용하여 자식 노드에 간단히 접근할 수 있다.
👉 바이너리 힙(Binary Heap)의 경우 배열의 첫 번째 요소를 root로 삼고 좌우 자식 노드들이 번갈아가며 배열에 들어간다.
👉 부모 노드의 값이 자식 노드의 값보다 크면 최대 힙(Max-Heap), 작으면 최소 힙(Min-Heap)이라고 한다.
🔴 [2, 4, 23, 12, 13]과 같은 배열로 된 힙 구조를 그림으로 나타내면 다음과 같다.
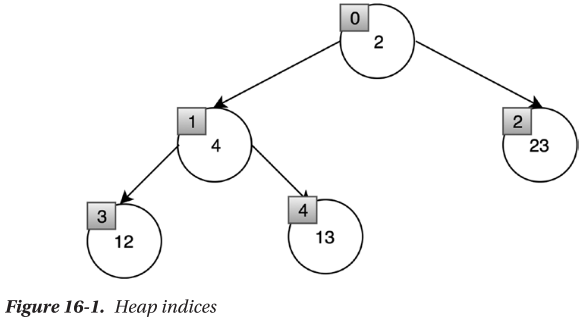
힙 인덱스
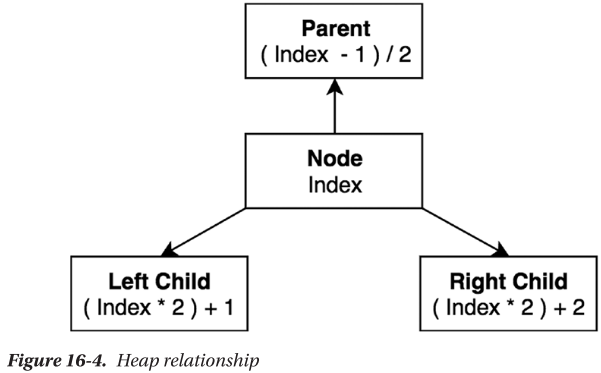
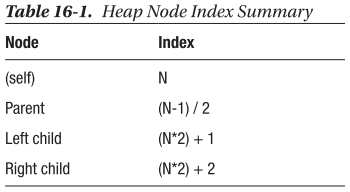
🔴 바이너리 힙 구조에서 각 노드에 접근하기 위해 활용하는 인덱스는 다음과 같다.

퍼컬레이션(Percolation): Bubbling Up and Down
👉 힙에 새로운 값이 추가되거나 힙에서 기존의 값이 제거되더라도 힙 구조는 유지되어야 한다. 이때 힙은 퍼컬레이션을 통해 자신의 구조를 유지한다.
👉 퍼컬레이션을 통해 힙 구조의 아이템들은 'bubble up'되거나 'bubble down'되면서 자신의 자리를 찾아간다. 퍼컬레이션의 시간 복잡도는 O(log2(n))이다.
힙 구현 코드
🔴 힙
힙
class Heap { constructor() { this.items = []; } swap(index1, index2) { const temp = this.items[index1]; this.items[index1] = this.items[index2]; this.items[index2] = temp; } parentIndex(index) { return Math.floor((index - 1) / 2); } leftChildIndex(index) { return index * 2 + 1; } rightChildIndex(index) { return index * 2 + 2; } parent(index) { return this.items[this.parentIndex(index)]; } leftChild(index) { return this.items[this.leftChildIndex(index)]; } rightChild(index) { return this.items[this.rightChildIndex(index)]; } peek(item) { return this.items[0]; } size() { return this.items.length; } }
👉 앞서 인덱스를 활용해서 부모, 왼쪽 자식, 오른쪽 자식을 반환함을 볼 수 있다.
🔴 최소 힙
최소 힙
// inherit helpers from heap by extends class MinHeap extends Heap { constructor(items) { super(items); } add(item) { this.items.push(item); this.bubbleUp(); } // removes the minimum element(the root) from heap and calls bubbleDown() to keep the min-heap order poll() { const item = this.items[0]; this.items[0] = this.items[this.items.length - 1]; this.items.pop(); this.bubbleDown(); return item; } bubbleDown() { let index = 0; while ( this.leftChild(index) && this.leftChild(index) < this.items[index] ) { let smallerIndex = this.leftChildIndex(index); if ( this.rightChild(index) && this.rightChild(index) < this.items[smallerIndex] ) { // if right is smaller, right swaps smallerIndex = this.rightChildIndex(index); } this.swap(smallerIndex, index); index = smallerIndex; } } bubbleUp() { let index = this.items.length - 1; while (this.parent(index) && this.parent(index) > this.items[index]) { this.swap(this.parentIndex(index), index); index = this.parentIndex(index); } } } console.log('===== MIN HEAPS ====='); const min = new MinHeap(); min.add(1); min.add(10); min.add(5); min.add(100); min.add(8); console.log('min poll', min.poll()); console.log('min poll', min.poll()); console.log('min poll', min.poll()); console.log('min poll', min.poll()); console.log('min poll', min.poll()); // ===== MIN HEAPS ===== // min poll 1 // min poll 5 // min poll 8 // min poll 10 // min poll 100
🔴 최대 힙
최대 힙
class MaxHeap extends Heap { constructor(items) { super(items); } add(item) { this.items.push(item); this.bubbleUp(); } // removes the maximum element(the root) from heap and calls bubbleDown() to keep the max-heap order poll() { const item = this.items[0]; this.items[0] = this.items[this.items.length - 1]; this.items.pop(); this.bubbleDown(); return item; } bubbleDown() { let index = 0; while ( this.leftChild(index) && this.leftChild(index) > this.items[index] ) { let biggerIndex = this.leftChildIndex(index); if ( this.rightChild(index) && this.rightChild(index) > this.items[biggerIndex] ) { // if right is bigger, right swaps biggerIndex = this.rightChildIndex(index); } this.swap(biggerIndex, index); index = biggerIndex; } } bubbleUp() { let index = this.items.length - 1; while (this.parent(index) && this.parent(index) < this.items[index]) { this.swap(this.parentIndex(index), index); index = this.parentIndex(index); } } } console.log('===== MAX HEAPS ====='); const max = new MaxHeap(); max.add(1); max.add(10); max.add(5); max.add(100); max.add(8); console.log('max poll', max.poll()); console.log('max poll', max.poll()); console.log('max poll', max.poll()); console.log('max poll', max.poll()); console.log('max poll', max.poll()); // ===== MAX HEAPS ===== // max poll 100 // max poll 10 // max poll 8 // max poll 5 // max poll 1
👉 bubbleUp과 bubbleDown을 주의 깊게 보자. 새로운 값은 배열의 맨 끝에 추가되므로 bubbleUp을 통해 밑에서 위로 올라가며 제 자리를 찾아가고, 값이 제거되었을 경우에는 bubbleDown을 통해 맨 뒤의 값을 맨 위로 올린 다음 내려가면서 제 자리를 찾는 식으로 동작한다.
👉 최소 힙을 기준으로 bubbleDown을 설명하자면, 맨 위의 요소가 왼쪽 자신보다 크다면 반복문과 swap 메서드를 통해 아래로 내린다. 그러다가 조건을 충족하지 않으면 바꾸기를 멈춘다. 반복문으로 탐색하는 와중에 왼쪽 자식이 오른쪽 자식보다 크다면 서로의 위치를 바꾼다. 최소값이 제거된 후 이런 과정을 통해 힙 구조가 남은 값을 기준으로 재정렬된다.
힙 정렬(Heap Sort)
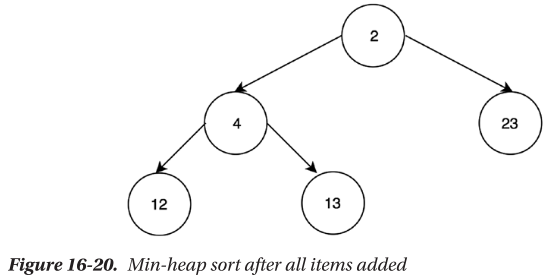
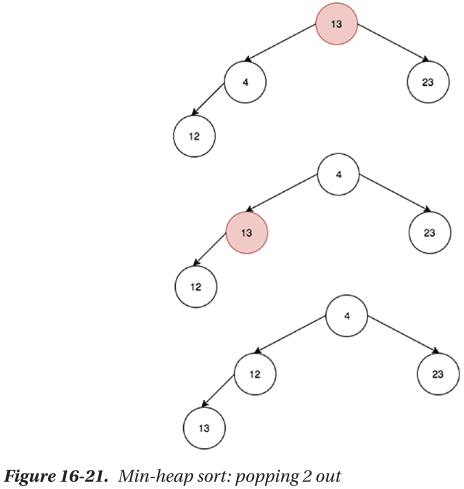
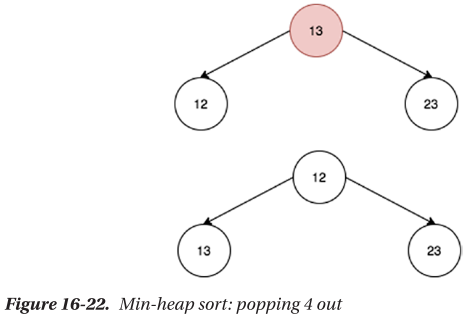
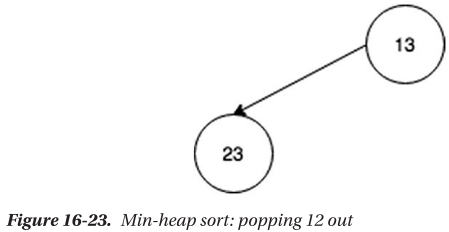
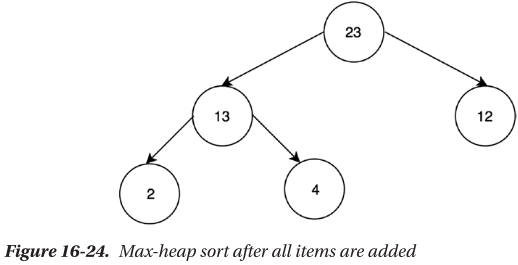
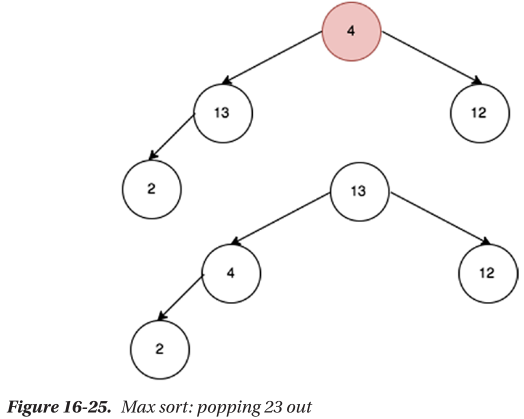
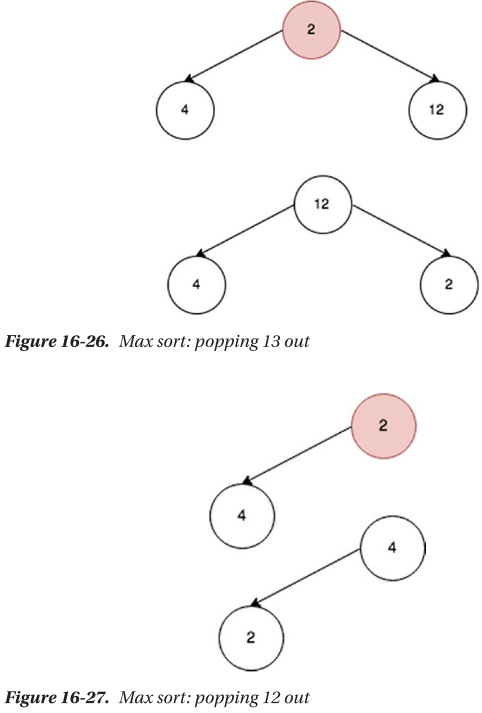
👉 힙 구조를 정렬하려면 간단히 pop 메서드를 호출하여 제거된 요소를 새로운 배열에 순서대로 담으면 된다. 이때 최소 힙은 오름차순, 최대 힙은 내림차순으로 정렬된다.
👉 힙 정렬의 시간복잡도는 퀵 정렬(Quick Sort)나 병합 정렬(Merge Sort)와 마찬가지로 O(nlog2(n))이다. 앞서 살펴본 퍼컬레이션을 통해 정렬을 구현하기 때문이다.
🔴 최소 힙을 통한 오름차순 정렬
🔴 최대 힙을 통한 내림차순 정렬
요약
- 힙은 트리처럼 생긴 데이터 구조로 배열로 구성된다.
- 힙에서 부모, 왼쪽 자식, 오른쪽 자식 요소를 얻기 위한 인덱스는 다음과 같다.
- 힙은 퍼컬레이션을 통해 구조를 유지한다. 새로운 노드가 추가되면 알맞은 구조가 될 때까지 'bubbles up'이 일어난다. 최소 힙이라면 가장 작은 노드, 최대 힙이라면 가장 큰 노드가 맨 위로 간다.
- 힙에 대한 노드 삽입, 삭제, 정렬의 시간 복잡도는 다음과 같다.

'👩💻 Programming > Algorithms & Data Structures' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료 구조] 트라이(Trie) (0) | 2023.01.30 |
|---|---|
| DFS/BFS (깊이 우선 탐색/너비 우선 탐색) (0) | 2023.01.16 |
| 힙 정렬(Heaps sort)에 대해 알아보자! (0) | 2022.06.23 |
| 하노이의 탑(Towers of Hanoi) (0) | 2022.04.07 |
| 재귀 알고리즘(Recursive Algorithms) (0) | 2022.04.07 |




댓글